Airfix A1351 1/35 Panzer IV Ausf H Mid Version*
39.00
$
<p>The German medium tank Panzerkampfwagen IV was developed in the late 1930s and was used extensively during WWII. The production of the Panzer IV Ausf. H started in June 1943. This version was designated the Sd. Kfz. 161/2. Compared to the previous variants, this model had Zimmerit paste on all the vertical surfaces of its armour in order to prevent adhesion of magnetic anti-tank mines.</p><p>The turret roof was reinforced from 10mm to 16 and 25mm segments. 5mm hull skirts and 8mm turret skirts were added for further protection, which resulted in the elimination of the vision ports on the hull side. Later on, the hull was also fitted with triangular supports for the easily damaged side skirts. Along with some other modifications, these additions to the design increased the tank's weight to 25 tonnes, and the maximum speed dropped to 16 km/h on cross country terrain.</p><h3>Specifications</h3><ul>
<li>Item Length - Without Packaging (cm): 20.1</li>
<li>Item Height - Without Packaging (cm): 7.66</li>
<li>Item Width - Without Packaging (cm): 8.2</li>
<li>Item Scale: 1:35</li>
<li>Contents (what's in the box) sets: Sprues & decals</li>
<li>Finish: Plastic</li>
<li>Number of Scheme options: 2</li>
<li>Skill Level: 3</li>
<li>Flying Hours: 3</li>
</ul>

Roden 804 1/35 Sov. KrAZ-214B Truck
29.00
$
<p>During WWII under the terms of the Lend-Lease agreement, apart from thousands of the well-known 'Studebakers', a limited number of Diamond and White heavy ballast tractors appeared in the USSR. These trucks made a great impression on the Soviet military, because the ZIS-5 and GAZ-AA, which Soviet industry had been producing since the pre-war period, could not compare with the American vehicles, which were able to haul a trailer loaded even with heavy tanks. </p>
<p>Immediately after the end of the war the Yaroslavl motor works, which had previously produced YAG-6 trucks in very small quantities, received an order to develop a new truck. So in 1947 appeared the YAZ-200, the first Soviet truck with a fourteen-cylinder diesel engine, and a year later, the YAZ-210 with a more powerful six-cylinder YAZ-206 diesel. These trucks began to figure in the inventory of the Soviet Army; however, the Army had need of a truck with much better characteristics, especially taking into consideration cross country ability. </p>
<p>So, in 1951 appeared the YAZ-214, a 6x6 truck which could carry 7 tonnes, and unusual single wheels '15,00-20' in diameter. The truck differed from its predecessors in featuring a new style of cabin, which clearly showed the influence of the designs of the American motor industry of the 1940's. Nevertheless this truck very quickly became irreplaceable in the Soviet Army, and the YAZ-214's entire production run of 1,265 went straight into military service. </p>
<p>In 1959, under the development plan for the motor industry, the government of the USSR decided to transfer equipment for truck manufacture from Yaroslavl to Minsk (biaxial trucks) and to the Ukrainian city of Kremenchug (triaxial trucks), where on the foundations of a small former agricultural machinery plant, a giant new factory was built to produce large trucks. So, the Russian YAZ gained a new Ukrainian identity. The trucks were initially given the name of 'Dnepr' (obviously, to denote the new locality of production), however this name did not last for long, and in 1964 all trucks from Kremenchug were designated 'KrAZ', in order not to stand out from the other streams of the Soviet motor industry. </p>
<p>The KrAZ showed few visible differences from its predecessor, except in the replacement of the stylized Yaroslavl bear cub on the hood by a nameplate in red and blue colors on the front radiator grille, which symbolized the flag of the Ukrainian SSR. In this form the truck was produced until 1963, when it was upgraded to the KrAZ-214B with an improved electrical system and a stronger hanger bracket. The production of this model lasted almost 5 years more, and in 1967 the KrAZ-214 was replaced on the assembly line by the next generation truck, the KrAZ-255. Overall, between 1959 and 1967 over 32,000 of the KrAZ-214 were produced in Kremenchug. </p>
<p>While the YAZ-214 was used only as a flat sided truck (except for the 2P5 Transporter-Erector-Launcher), its successor the KrAZ-214 had much more widespread usage in different versions. On the chassis as supplied from the plant in Kremenchug, various installations were assembled in different munitions factories. The most common were engineering trucks - the PMP pontoon truck, the TMM bridge layer, the E-305 power-shovel, and the FM truck-mounted crane (dual action firing mechanism). Various containers could be fitted to the KrAZ-214 for transportation of fuel for the rocket troops, including caustic rocket propellant. </p>
<p>Apart from the USSR, the KrAZ-214 was widely exported to other socialist countries - East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Poland, Hungary, Romania, Vietnam, and also to Egypt and Algeria, where they were used by the armies of all those countries. Some KrAZ-214 trucks are around 50 years old, and they are still operated in Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Bulgaria and Germany. </p>

Trumpeter 09525 1/35 Russian T-80U*
38.00
$
<p>The T-80U main battle tank is a later modified version of the T-80, which entered service with the Soviet Army in 1985.</p>
<p>The T-80U has a cast turret with a welded body and a low projection area. Compared to the early T-80B series, the armor protection capability has been greatly improved. The main armor is a composite armor of various materials, plus "contact" type-5 reaction armor. The car is also equipped with an automatic fire suppression device and a nuclear biochemical protection system.</p>
<p>The main weapon of the T-80U is a two-way stable 125mm smoothbore with an automatic loader. It is equipped with shelling armor-piercing projectiles, armor-piercing projectiles and high-explosive grenade. It can also fire a 9 M119M anti-tank missile (known as the AT-11 "sniper" in the West). The missile has a maximum range of 5 kilometers and can also attack low-altitude helicopters. The auxiliary weapon is a 7.62 mm coaxial machine gun and a 12.7 mm high-altitude machine gun at the top of the turret.</p>
<p>The original production plan for the T-80U main battle tank was to install the GTD-1000 TF gas turbine with a power of 1,100 hp. Since the early 1990s, the GTD-1250 gas turbine has been replaced with a power of 1250 horsepower. </p>

Trumpeter 02313 1/35 German 17cm Kanone 18 Heavy Gun
37.00
$
<p>The 203 mm Howitzer Model 1931 (known unofficially as the B4) was the heaviest of the field weapons used by the Soviets between 1941 and 1945. The distinctive feature of the B4 was the two tracked bogies which allowed the heavy weapon to move over soft ground and snow unlike other contemporary weapons that were all but impossible to move in such conditions. </p>
<p>The Howitzer was not powered but could be towed short distances fully assembled while it was broken down into smaller loads for longer distance travel by road or rail. </p>
<p>The B4 was a very powerful weapon but also had a slow rate of fire due to the large heavy projectiles and came fitted with a shell handling crane to assist the crew during loading. It was used primarily to attack fortifications and bunkers with a range of 18 km (11 miles) for its 100 kg (220.46 lb) shell. </p>
<p>There are numerous period photos of the B4 in action but none as dramatic as those taken during the battle for Berlin in 1945 where the massive B4 was used at almost point blank range for such a weapon and must have been a fearful sight and sound for the defenders on the receiving end at such ranges. </p>
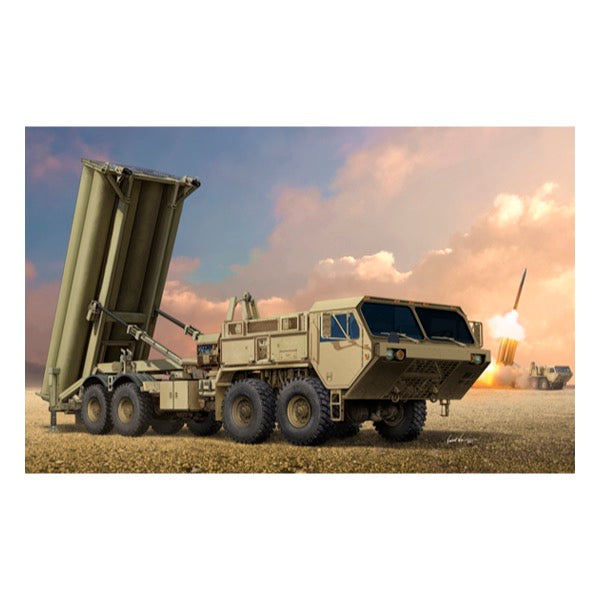

Trumpeter 01054 1/35 Terminal High Altitude Area Defence (THAAD)*
83.00
$
<p>Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD), formerly Theater High Altitude Area Defense, is a United States Army anti-ballistic missile system designed to shoot down short, medium, and intermediate range ballistic missiles in their terminal phase using a hit-to-kill approach. The missile carries no warhead but relies on the kinetic energy of the impact to destroy the incoming missile. A kinetic energy hit minimizes the risk of exploding conventional warhead ballistic missiles, and nuclear tipped ballistic missiles will not explode upon a kinetic energy hit, although chemical or biological warheads may disintegrate or explode and pose a risk of contaminating the environment. THAAD was designed to hit Scuds and similar weapons. According to a statement released On July 7, 2016, the Pentagon announced it is conducting formal feasibility studies for placement of a THAAD battery in South Korea “as a defensive measure to ensure the security of the ROK(Republic of Korea) and its people and to protect alliance military forces from North Korea’s weapons of mass destruction and ballistic missile threats.”After North Korea's reported launch of three Rodong missiles near the coast of Japan on September 5, 2016, Beijing publicly voiced opposition to such a deployment, citing concerns that it would not be "conducive to strategic stability in the region, and could intensify disputes.</p>
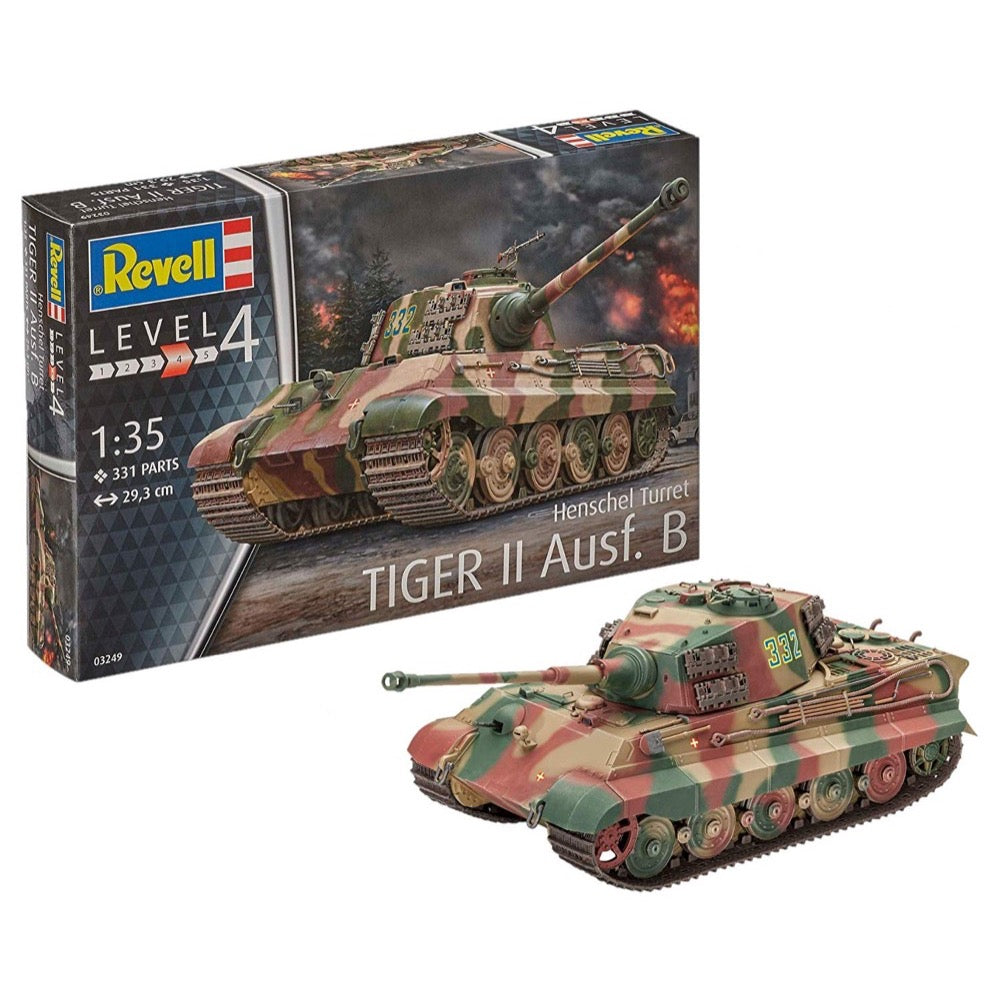

Revell 03249 1/35 Tiger II AUSF.B Henschel Turret
31.00
$
<p>High quality, precision <a>plastic model kit</a>. <a>Paint</a> and <a>glue</a> not included. Requires assembly and painting. For intermediate to advanced skill modellers.</p>